Deep Dive: Analyzing Connectivity#
This tutorial will guide you through the process of querying and analyzing connectivity data using the CRANTpy package. We will cover
how to retrieve synapse data
filter synapse data, and
visualize the results.
Let’s get started by setting up our environment.
# Import CRANTpy and other necessary libraries
import crantpy as cp
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import navis
# Set up logging to see progress
cp.set_logging_level("WARNING")
navis.set_loggers('WARNING')
print("CRANTpy loaded successfully!")
print(f"Default dataset: {cp.CRANT_DEFAULT_DATASET}")
CRANTpy loaded successfully!
Default dataset: latest
1. Authentication Setup#
Before we can access the data, we need to authenticate with the CAVE service. This is typically a one-time setup.
# Generate and save authentication token (uncomment if first time)
# cp.generate_cave_token(save=True)
# Test connection
try:
client = cp.get_cave_client()
print(f"Successfully connected to datastack: {client.datastack_name}")
print(f"Server: {client.server_address}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Connection failed: {e}")
print("Please run: cp.generate_cave_token(save=True)")
Successfully connected to datastack: kronauer_ant
Server: https://proofreading.zetta.ai
2. Understanding Automatic ID Updates and Caching#
Why ID Updates Matter#
In CAVE/FlyWire, neuron segmentations are constantly being refined through proofreading. When neurons are merged or split, their root IDs change. However, the synapse tables always use the latest root IDs at the time of materialization.
This means that if you have an older root ID from a previous version, querying with it directly might:
Return no results (if the neuron was merged into another)
Return incomplete results (if part of it was split off)
Give you data for the wrong neuron (if the ID now refers to something else)
Automatic ID Updates#
To solve this problem, CRANTpy automatically updates all root IDs to their latest versions before querying connectivity data. This happens by default in all connectivity functions:
get_synapses()- Updates both pre_ids and post_idsget_adjacency()- Updates IDs before querying synapsesget_connectivity()- Updates neuron_ids before queryingget_synapse_counts()- Updates neuron_ids before countingattach_synapses()- Updates skeleton IDs before attaching
How Caching Works#
ID updates could be slow if done repeatedly, so CRANTpy uses intelligent per-ID caching:
Per-ID Granularity: Each individual ID’s update result is cached separately
Partial Reuse: If you query
[ID1, ID2, ID3]and then[ID2, ID3, ID4], the cached results for ID2 and ID3 are reusedAutomatic Expiration: Cached results expire after a configurable duration (default: 7 days)
Preserved Metadata: All columns (old_id, new_id, confidence, changed) are preserved in the cache
Performance Impact: For fully cached queries, you can see speedups of over 2500x! Even with partial cache hits, the overhead is minimal (1-2 seconds).
Controlling ID Updates#
While automatic updates are enabled by default (update_ids=True), you can disable them if needed:
# Default behavior - IDs are automatically updated (recommended)
synapses = cp.get_synapses(pre_ids=[123, 456])
# Disable updates - only use if you're certain IDs are current
synapses = cp.get_synapses(pre_ids=[123, 456], update_ids=False)
⚠️ Warning: Only disable automatic updates if you’re absolutely certain your IDs are current. Using outdated IDs can lead to incorrect connectivity results!
# Example: See ID updates in action
import time
# Get some neuron IDs
sample_criteria = cp.NeuronCriteria(cell_class='olfactory_projection_neuron', side='right', tract='mALT')
sample_ids = sample_criteria.get_roots()[:3].astype(int).tolist()
print("First query - IDs will be updated and cached:")
start = time.time()
result1 = cp.get_synapses(pre_ids=sample_ids, threshold=5)
time1 = time.time() - start
print(f" Query completed in {time1:.2f} seconds")
print(f" Found {len(result1)} synapses")
print("\nSecond query - Uses cached ID updates:")
start = time.time()
result2 = cp.get_synapses(pre_ids=sample_ids, threshold=5)
time2 = time.time() - start
print(f" Query completed in {time2:.2f} seconds")
print(f" Found {len(result2)} synapses")
print(f"\nSpeedup from caching: {time1/time2:.1f}x faster!")
print("\nNote: The first query includes both ID update time and synapse retrieval.")
print("The second query still retrieves synapses but skips the ID update step.")
Managing Caches#
If you ever need to clear the ID update cache (for example, after a new materialization), you can use:
# Clear just the ID update cache
cp.clear_global_cache('update_ids_cache')
# Clear all caches
cp.clear_all_caches()
The cache automatically expires after 7 days by default, but manual clearing can be useful if you know there have been significant proofreading changes.
3. Querying Synapses#
Outputs of Olfactory Projection Neurons#
Let’s start by sampling three olfactory projection neurons from the right mALT, and then use the get_synapses() function to find their postsynaptic partners.
pre_ids=sample_idsfilters for synapses downstream of our olfacotry projection neuronsthreshold=3only preserves connections between neurons with at least 3 synapsesmaterialization='latest'uses the most recent version of the synapse tablemin_size=10thresholds on the synapse sizereturn_pixels=Trueensures that the coordinates in the table are in pixels, not nanometersupdate_ids=True(default) automatically updates IDs to their latest versions
# Get a sample of olfactory projection neurons
opn_criteria = cp.NeuronCriteria(cell_class='olfactory_projection_neuron', side='right', tract='mALT')
opn_ids = opn_criteria.get_roots()
print(f"Found {len(opn_ids)} olfactory projection neurons")
# Select a few for detailed analysis
sample_ids = opn_ids[:3]
print(f"\nSample neurons for detailed analysis:")
for i, neuron_id in enumerate(sample_ids, 1):
print(f" {i}. {neuron_id}")
# Query synapses downstream of the sample neurons
synapses = cp.get_synapses(pre_ids=sample_ids, threshold=3, materialization='latest', min_size=10, return_pixels=True).sort_values(by=['size'], ascending=False)
synapses
2025-10-09 21:21:11 - WARNING - Multiple supervoxel IDs found for 129 root IDs. Using first occurrence for each.
Found 34 olfactory projection neurons
Sample neurons for detailed analysis:
1. 576460752773799604
2. 576460752722298426
3. 576460752680204173
| pre_pt_root_id | post_pt_root_id | id | created | superceded_id | valid | size | pre_pt_supervoxel_id | post_pt_supervoxel_id | pre_pt_position | post_pt_position | ctr_pt_position | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2452 | 576460752722298426 | 576460752699041619 | 7796505 | 2025-03-27 13:34:35.700037+00:00 | NaN | t | 403 | 72691531949599416 | 72691531949596725 | [11392, 11784, 3000] | [11374, 11786, 2998] | [11442, 11817, 3000] |
| 144 | 576460752722298426 | 576460752706238547 | 25500275 | 2025-03-27 13:34:35.700037+00:00 | NaN | t | 375 | 73043375402249556 | 73043375402302436 | [17372, 11816, 2045] | [17368, 11838, 2047] | [17374, 11836, 2052] |
| 2604 | 576460752722298426 | 576460752765476144 | 20274550 | 2025-03-27 13:34:35.700037+00:00 | NaN | t | 367 | 72973006725106953 | 72973006725115267 | [15480, 11684, 2279] | [15494, 11706, 2279] | [15502, 11701, 2277] |
| 2470 | 576460752722298426 | 576460752706238547 | 25608007 | 2025-03-27 13:34:35.700037+00:00 | NaN | t | 329 | 73043375468665541 | 73043375468668812 | [17312, 11818, 2052] | [17316, 11846, 2052] | [17332, 11844, 2055] |
| 2569 | 576460752722298426 | 576460752756460946 | 45517299 | 2025-03-27 13:34:35.700037+00:00 | NaN | t | 318 | 73396593378155594 | 73396593378158596 | [22152, 32672, 1431] | [22130, 32680, 1432] | [22148, 32678, 1435] |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 1062 | 576460752773799604 | 576460752690968107 | 75114322 | 2025-03-27 13:34:35.700037+00:00 | NaN | t | 10 | 74030187222317847 | 74030187222329021 | [31622, 36238, 2531] | [31616, 36254, 2532] | [31624, 36244, 2534] |
| 203 | 576460752722298426 | 576460752659677339 | 45507925 | 2025-03-27 13:34:35.700037+00:00 | NaN | t | 10 | 73396593378192012 | 73396593378194720 | [22128, 32144, 1447] | [22108, 32136, 1447] | [22122, 32130, 1446] |
| 1859 | 576460752773799604 | 576460752768105504 | 88939778 | 2025-03-27 13:34:35.700037+00:00 | NaN | t | 10 | 74450612913565186 | 74450612913567407 | [37328, 10236, 2171] | [37310, 10212, 2173] | [37320, 10222, 2173] |
| 1909 | 576460752773799604 | 576460752743279908 | 96841840 | 2025-03-27 13:34:35.700037+00:00 | NaN | t | 10 | 74661650627953715 | 74661650627966625 | [40926, 8896, 2935] | [40950, 8894, 2938] | [40940, 8896, 2937] |
| 219 | 576460752722298426 | 576460752671252568 | 44936261 | 2025-03-27 13:34:35.700037+00:00 | NaN | t | 10 | 73396524658445730 | 73396524658440600 | [21708, 31538, 1345] | [21718, 31562, 1345] | [21724, 31550, 1345] |
2998 rows × 12 columns
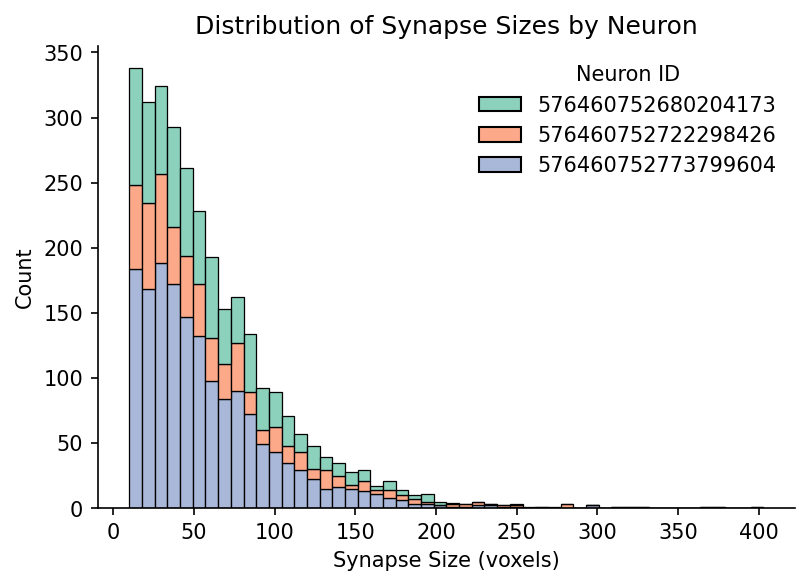
Let’s first count the number of synapses for each of our root IDs
synapses.groupby('pre_pt_root_id').size().reset_index(name='num_synapses')
| pre_pt_root_id | num_synapses | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 576460752680204173 | 801 |
| 1 | 576460752722298426 | 582 |
| 2 | 576460752773799604 | 1615 |
Plot distribution of synapse size#
Now let’s plot the distribution of synapses sizes for each neuron
f, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(6, 4), dpi=150)
sns.histplot(data=synapses, x='size', hue='pre_pt_root_id', multiple='stack', bins=50, ax=ax, stat='count', legend=True, palette='Set2')
ax.set_xlabel('Synapse Size (voxels)')
ax.set_ylabel('Count')
ax.set_title('Distribution of Synapse Sizes by Neuron')
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
# Customize legend
legend = ax.get_legend()
legend.set_title('Neuron ID') # Change legend title
legend.set_frame_on(False) # Turn off legend frame
plt.show()
Inspect synapses in the EM data#
Now let’s plot the raw EM data centered at the three largest synapses and inspect whether we see synaptic vesicles.
# Plot EM image around the detected synapses
image_size = 500
top_synapse_coords = synapses[['ctr_pt_position']].head(3).values.tolist()
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(15, 5))
for ax, coords in zip(axes, top_synapse_coords):
x_center, y_center, z_center = coords[0]
img = cp.plot_em_image(x_center, y_center, z_center, size=image_size)
ax.scatter(image_size//2, image_size//2, marker='x', color='red', s=100)
ax.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
ax.set_title(f"Synapse at ({x_center}, {y_center}, {z_center})")
ax.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Downloading Bundles: 100%|██████████| 5/5 [00:00<00:00, 5.85it/s]
Decompressing: 100%|██████████| 9/9 [00:00<00:00, 1222.67it/s]
Downloading Bundles: 100%|██████████| 5/5 [00:01<00:00, 3.29it/s]
Decompressing: 100%|██████████| 9/9 [00:00<00:00, 101.64it/s]
Downloading Bundles: 100%|██████████| 5/5 [00:03<00:00, 1.29it/s]
Decompressing: 100%|██████████| 9/9 [00:00<00:00, 45.13it/s]
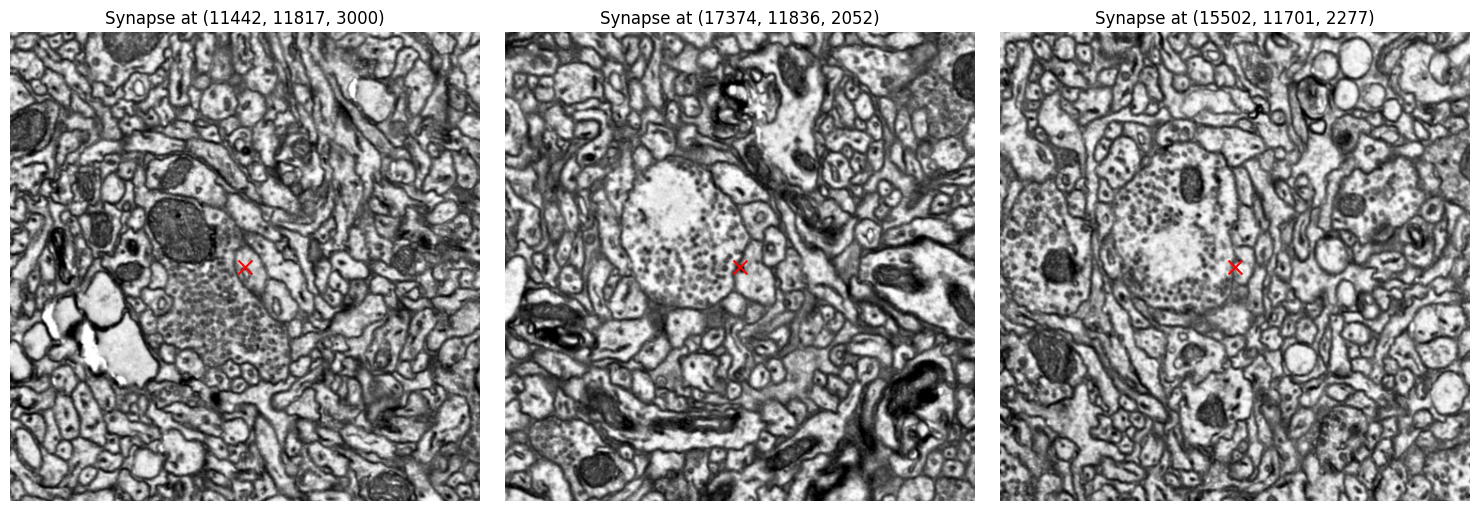
The presynaptic neurons clearly have lots of vesicles!
4. Querying Adjacency#
Inputs to Olfactory Projection Neurons#
Instead of getting the full synapse table, we can get an adjacency matrix of synaptic connections between neurons using the get_adjacency function:
post_ids=sample_idsexclusively looks for inputs to the neuronssymmetric=Falseensures that rows represent pre-synaptic neurons and columns post-synaptic neurons.IDs are automatically updated before querying (can be disabled with
update_ids=False)
# Get a sample of olfactory projection neurons
opn_criteria = cp.NeuronCriteria(cell_class='olfactory_projection_neuron', side='right', tract='mALT')
opn_ids = opn_criteria.get_roots()
sample_ids = opn_ids[:5]
# Get adjacency matrix for the sample neurons
adjacency = cp.get_adjacency(post_ids=sample_ids, threshold=3, symmetric=False)
print(f"Adjacency matrix shape: {adjacency.shape}")
print(f"Identified {adjacency.shape[0]} input neurons connected to our {adjacency.shape[1]} sample PNs.")
2025-10-09 21:21:47 - WARNING - Multiple supervoxel IDs found for 129 root IDs. Using first occurrence for each.
Adjacency matrix shape: (124, 5)
Identified 124 input neurons connected to our 5 sample PNs.
Let’s sort the rows and columns and plot a heatmap to visualize our adjacency matrix.
# Sort columns by the maximum connections
col_sums = adjacency.sum(axis=0)
sorted_indices = col_sums.sort_values(ascending=False).index
adjacency = adjacency[sorted_indices]
# sort rows by the location of their maximum connection
row_max_locs = adjacency.values.argmax(axis=1)
sorted_row_indices = np.argsort(row_max_locs)
adjacency = adjacency.iloc[sorted_row_indices]
# Plot heatmap of connections
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 10), dpi=150)
plt.imshow(adjacency.values, aspect='auto', cmap='viridis')
plt.colorbar(label='Number of Synapses')
plt.xlabel('PNs')
plt.ylabel('Inputs')
plt.xticks(ticks=np.arange(len(adjacency.columns)), labels=adjacency.columns, rotation=0, fontsize=3)
plt.yticks(ticks=np.arange(len(adjacency.index)), labels=adjacency.index, fontsize=3)
plt.show()
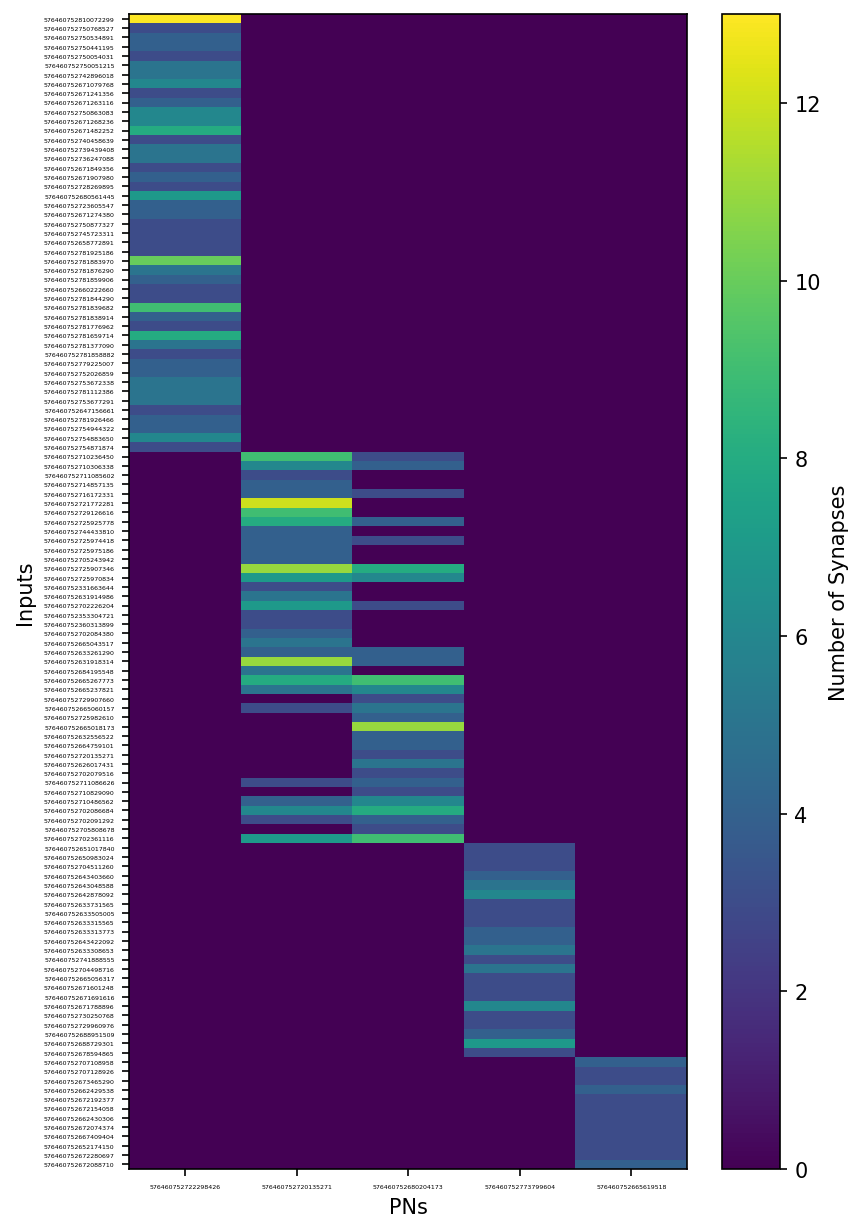
By eye, it looks like two of these PNs share the same glomerulus!
Querying Adjacency within the Central Complex#
Now let’s query connectivity in the central complex.
First we will collect determine our neurons of interest using NeuronCriteria:
# Get neurons belonging to the central complex
cx_neurons = cp.NeuronCriteria(cell_class=['EBc', 'ER', 'FBt', 'PBt'], region='CX')
print(f"Filtered to {len(cx_neurons.get_roots())} neurons in selected classes.")
cx_annotations = cp.get_annotations(cx_neurons)
cx_annotations['cell_class'].value_counts().reset_index()
Filtered to 333 neurons in selected classes.
| cell_class | count | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | ER | 137 |
| 1 | FBt | 91 |
| 2 | PBt | 64 |
| 3 | EBc | 47 |
Now when we use get_adjacency we restrict both pre_ids and post_ids to our predefined NeuronCriteria to only query connections betweeen our neurons of interest.
adjacency = cp.get_adjacency(pre_ids=cx_neurons, post_ids=cx_neurons, threshold=3, symmetric=True)
2025-10-09 21:22:30 - WARNING - Multiple supervoxel IDs found for 129 root IDs. Using first occurrence for each.
And now we plot a heatmap grouped by cell class:
# Create neuron to class mapping using the existing cx_annotations
# Convert root_id to int to match adjacency matrix data type
cx_annotations_int = cx_annotations.copy()
cx_annotations_int['root_id'] = cx_annotations_int['root_id'].astype(int)
neuron_to_class = cx_annotations_int.set_index('root_id')['cell_class'].to_dict()
# Create sorted lists of neuron IDs grouped by class
class_groups = {}
for neuron_id in adjacency.index:
cell_class = neuron_to_class.get(neuron_id, 'Unknown')
if cell_class not in class_groups:
class_groups[cell_class] = []
class_groups[cell_class].append(neuron_id)
# Sort classes by number of neurons (largest first)
sorted_classes = sorted(class_groups.keys(), key=lambda x: len(class_groups[x]), reverse=True)
sorted_neuron_ids = []
for cls in sorted_classes:
sorted_neuron_ids.extend(sorted(class_groups[cls]))
# Reorder the adjacency matrix
adjacency_sorted = adjacency.loc[sorted_neuron_ids, sorted_neuron_ids]
# Create the heatmap using seaborn
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6), dpi=200)
ax = sns.heatmap(adjacency_sorted.values,
cmap='coolwarm',
cbar_kws={'label': 'Number of Synapses'},
square=True)
# Add class boundaries
class_boundaries = []
current_pos = 0
for cls in sorted_classes:
current_pos += len(class_groups[cls])
class_boundaries.append(current_pos)
# Draw lines to separate classes
for boundary in class_boundaries[:-1]: # Don't draw the last boundary
ax.axhline(boundary, color='white', linewidth=2, alpha=0.8)
ax.axvline(boundary, color='white', linewidth=2, alpha=0.8)
# Create class tick labels
class_positions = []
current_pos = 0
for cls in sorted_classes:
class_size = len(class_groups[cls])
class_positions.append(current_pos + class_size/2)
current_pos += class_size
# Set tick labels to show classes instead of individual neuron IDs
ax.set_xticks(class_positions)
ax.set_xticklabels([f"{cls} (n={len(class_groups[cls])})" for cls in sorted_classes],
rotation=45, ha='right', fontsize=10)
ax.set_yticks(class_positions)
ax.set_yticklabels([f"{cls} (n={len(class_groups[cls])})" for cls in sorted_classes],
rotation=0, fontsize=10)
# Rows are pre-synaptic neurons, columns are post-synaptic neurons. Add x and y labels
ax.set_xlabel('Post-synaptic')
ax.set_ylabel('Pre-synaptic')
plt.title('Central Complex Connectivity Matrix')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
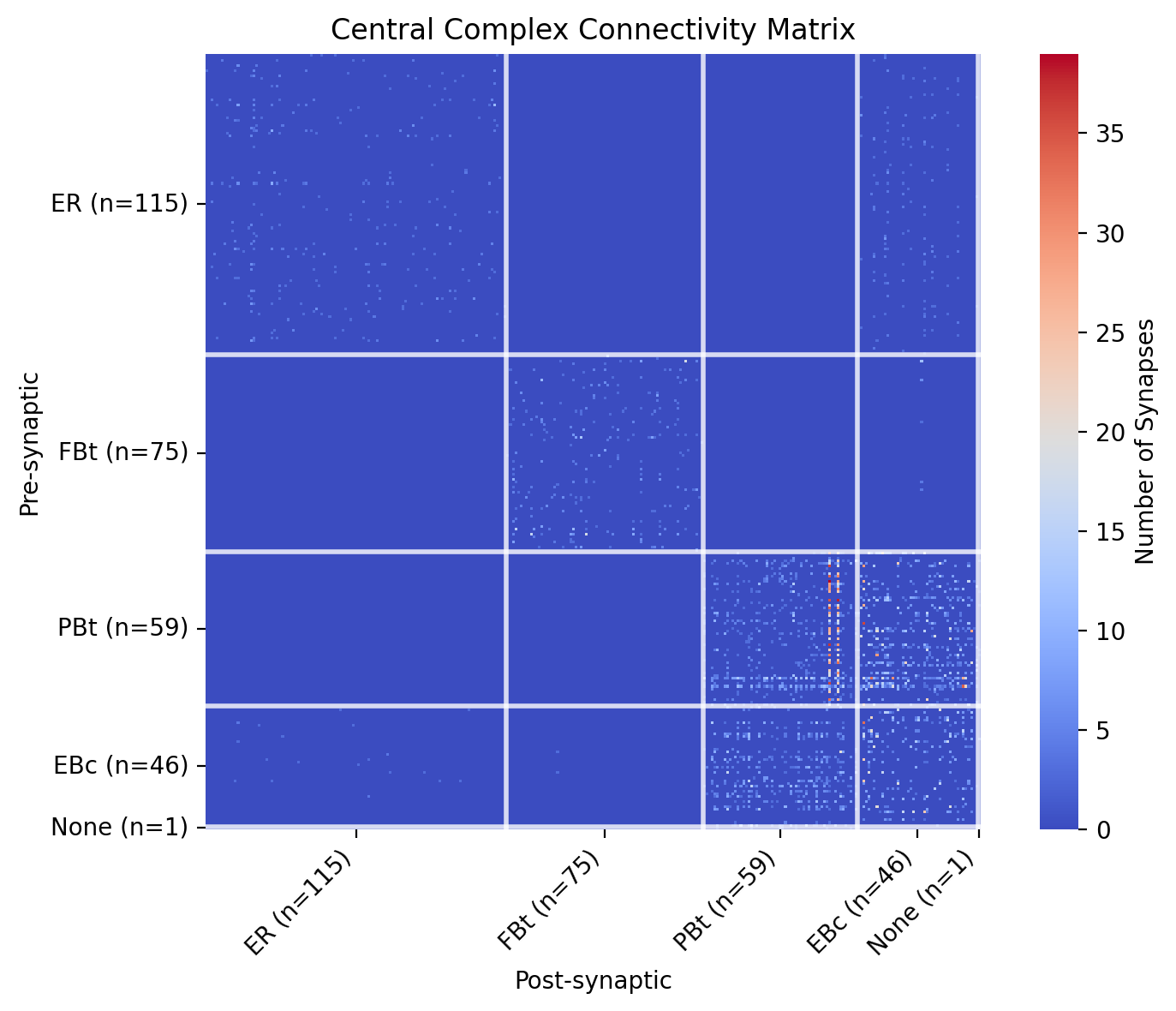
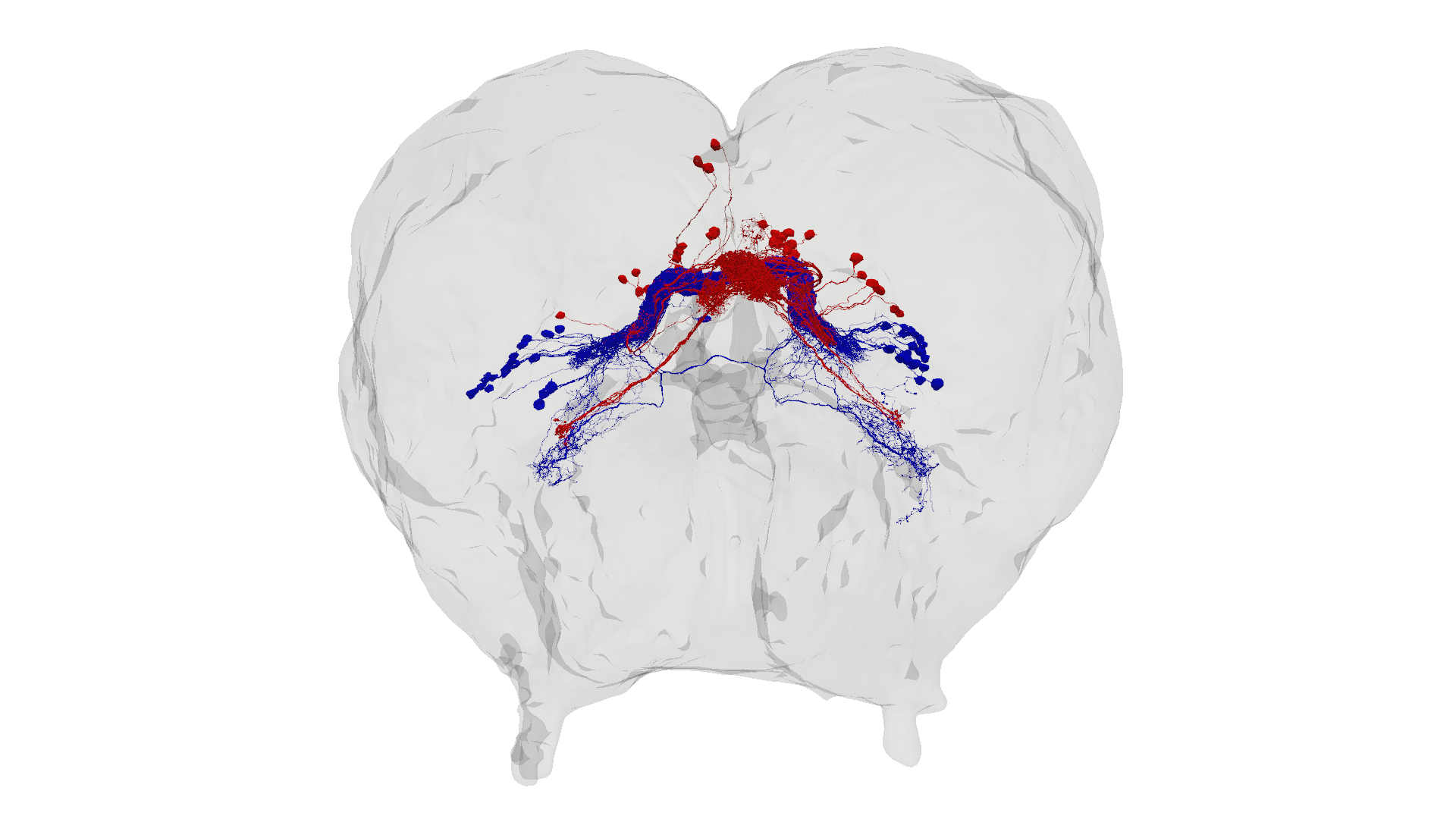
It’s clear from the heatmap that PBt and EBc populations are connected. Let’s isolate all of the EBc and PBt neurons and visualize them in the brain mesh.
# Isolate neuron subtypes
ebc_neurons = cx_annotations[cx_annotations['cell_class'] == 'EBc']['root_id'].astype(int).tolist()
pbt_neurons = cx_annotations[cx_annotations['cell_class'] == 'PBt']['root_id'].astype(int).tolist()
print(f"Found {len(ebc_neurons)} EBc neurons and {len(pbt_neurons)} PBt neurons.")
# Combine neuron IDs
combined_ids = ebc_neurons + pbt_neurons
# Define colors
neuron_colors = ['red' for _ in ebc_neurons] + ['blue' for _ in pbt_neurons]
# Plot the brain mesh scene
plotter = cp.get_brain_mesh_scene(combined_ids, backend='static', neuron_mesh_colors=neuron_colors)
plotter.window_size = (1920, 1080)
plotter.zoom_camera(1.5)
plotter.show()
Found 47 EBc neurons and 64 PBt neurons.
5. Querying Connectivity#
Another way of getting synapse information is using the get_connectivity function.
This function does not take a separate pre and post inputs, but you can specify whether to include upstream or downstream connections.
Here we query all of the synapses downstream and upstream of a single neuron and then plot the annotations for its connections.
Like all connectivity functions, IDs are automatically updated to their latest versions.
sample_id = 576460752732847432
print(f"Querying downstream connections for neuron ID {sample_id} of class {cp.get_annotations(sample_id)['cell_class'].values[0]}")
downstream_connections = cp.get_connectivity(neuron_ids=sample_id, upstream=False, downstream=True, threshold=5)
downstream_connections
Querying downstream connections for neuron ID 576460752732847432 of class PBt
| pre | post | weight | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 576460752732847432 | 576460752758099375 | 40 |
| 1 | 576460752732847432 | 576460752664985320 | 33 |
| 2 | 576460752732847432 | 576460752689030141 | 30 |
| 3 | 576460752732847432 | 576460752752135087 | 28 |
| 4 | 576460752732847432 | 576460752758006191 | 27 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 175 | 576460752732847432 | 576460752686098695 | 5 |
| 176 | 576460752732847432 | 576460752681077443 | 5 |
| 177 | 576460752732847432 | 576460752680886087 | 5 |
| 178 | 576460752732847432 | 576460752672839224 | 5 |
| 179 | 576460752732847432 | 576460752792903537 | 5 |
180 rows × 3 columns
Now we can easily add annotations, like post_cell_class, to these postsynaptic partners:
# Get annotations for postsynaptic neurons
annotations = cp.get_annotations(downstream_connections['post'].unique().tolist()).reset_index()
annotations['root_id'] = annotations['root_id'].astype(int)
# Add cell class to downstream connections, Fill in missing values with 'Unknown'
downstream_connections['post_cell_class'] = downstream_connections['post'].map(annotations.set_index('root_id')['cell_class'])
downstream_connections['post_cell_class'] = downstream_connections['post_cell_class'].fillna('Unknown')
downstream_connections
| pre | post | weight | post_cell_class | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 576460752732847432 | 576460752758099375 | 40 | Unknown |
| 1 | 576460752732847432 | 576460752664985320 | 33 | EBc |
| 2 | 576460752732847432 | 576460752689030141 | 30 | EBc |
| 3 | 576460752732847432 | 576460752752135087 | 28 | Unknown |
| 4 | 576460752732847432 | 576460752758006191 | 27 | EBc |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 175 | 576460752732847432 | 576460752686098695 | 5 | FBc |
| 176 | 576460752732847432 | 576460752681077443 | 5 | Unknown |
| 177 | 576460752732847432 | 576460752680886087 | 5 | Unknown |
| 178 | 576460752732847432 | 576460752672839224 | 5 | PBt |
| 179 | 576460752732847432 | 576460752792903537 | 5 | Unknown |
180 rows × 4 columns
Now for each postsynaptic cell class, let’s plot the number of connections and their average weight.
# Plot number of connections and average weight by cell class
summary = downstream_connections.groupby('post_cell_class').agg(
num_connections=('post', 'count'),
avg_weight=('weight', 'mean')
).reset_index().sort_values(by='num_connections', ascending=False)
# Plotting
f, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(8, 3), dpi=150)
ax[0].bar(summary['post_cell_class'], summary['num_connections'], color='skyblue')
ax[0].set_ylabel('Number of Connections')
ax[0].spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax[0].spines['right'].set_visible(False)
ax[1].bar(summary['post_cell_class'], summary['avg_weight'], color='salmon')
ax[1].set_ylabel('Average Weight')
ax[1].spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax[1].spines['right'].set_visible(False)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
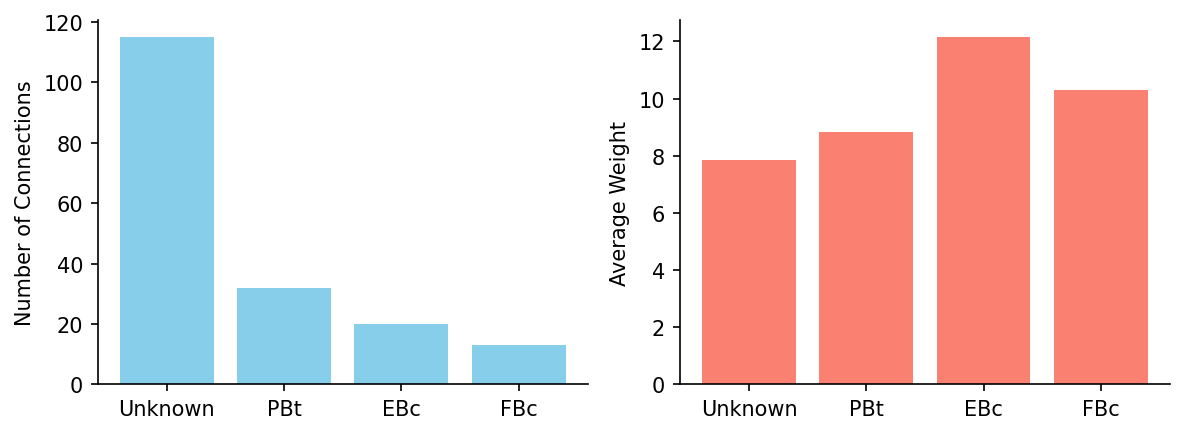
6. Synapse Counts#
If we don’t care about the identity of the synaptic partners and just the number of connections, we can use the function get_synapse_counts.
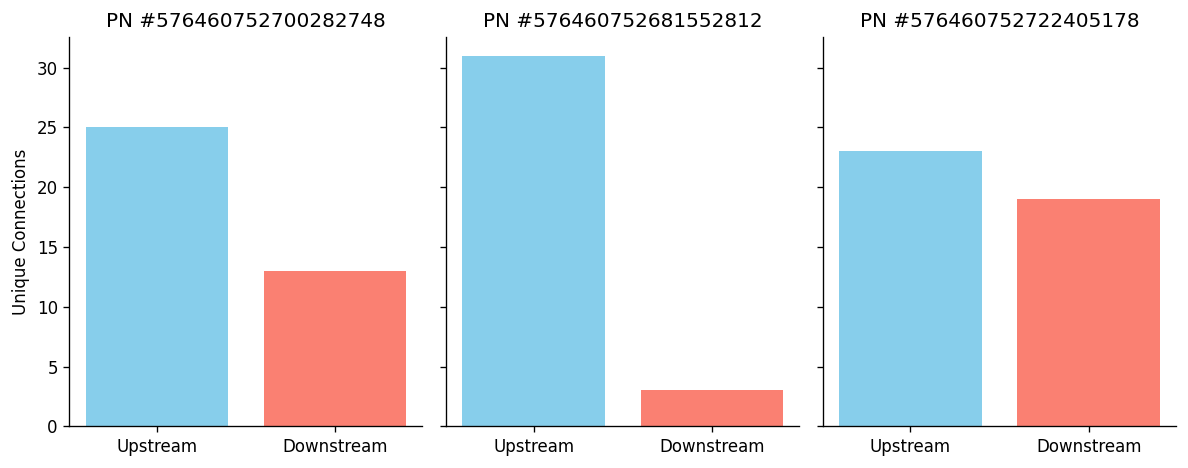
Here we sample 5 olfactory projection neurons from the left mALT tract, retrieve the synapse counts and plot the number of upstream and downstream connections.
All neuron IDs are automatically updated before counting synapses.
# Get a sample of olfactory projection neurons
opn_criteria = cp.NeuronCriteria(cell_class='olfactory_projection_neuron', side='left', tract='mALT')
opn_ids = opn_criteria.get_roots()
# Select a few for synapse count analysis
sample_ids = opn_ids[:3].astype(int).tolist()
synapse_counts = cp.get_synapse_counts(neuron_ids=sample_ids, threshold=5)
synapse_counts
2025-10-09 21:26:16 - WARNING - Multiple supervoxel IDs found for 129 root IDs. Using first occurrence for each.
| pre | post | |
|---|---|---|
| neuron_id | ||
| 576460752700282748 | 25 | 13 |
| 576460752681552812 | 31 | 3 |
| 576460752722405178 | 23 | 19 |
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(10, 4), sharey=True, dpi=120)
for ax, row in zip(axes, synapse_counts.iterrows()):
upstream_count = row[1]['pre']
downstream_count = row[1]['post']
ax.bar(['Upstream', 'Downstream'], [upstream_count, downstream_count], color=['skyblue', 'salmon'])
ax.set_title(f"PN #{row[0]}")
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
axes[0].set_ylabel('Unique Connections')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()