CRANTpy Tutorial: Exploring the Ant Brain Connectome#
This tutorial will guide you through the main features of CRANTpy, showing you how to:
Query neurons based on anatomical and functional criteria
Access morphological data including meshes and skeletons
Visualize neurons in 2D
Work with different dataset versions
Let’s start by importing CRANTpy and setting up the environment.
# Import CRANTpy and other necessary libraries
import crantpy as cp
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
# Set up logging to see progress
cp.set_logging_level("WARNING") # Options: DEBUG, INFO, WARNING, ERROR, CRITICAL
print("CRANTpy loaded successfully!")
print(f"Default dataset: {cp.CRANT_DEFAULT_DATASET}")
CRANTpy loaded successfully!
Default dataset: latest
1. Authentication Setup#
Before we can access the data, we need to authenticate with the CAVE service. This is typically a one-time setup.
# Generate and save authentication token (uncomment if first time)
# cp.generate_cave_token(save=True)
# Test connection
try:
client = cp.get_cave_client()
print(f"Successfully connected to datastack: {client.datastack_name}")
print(f"Server: {client.server_address}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Connection failed: {e}")
print("Please run: cp.generate_cave_token(save=True)")
Successfully connected to datastack: kronauer_ant
Server: https://proofreading.zetta.ai
2. Exploring Available Data#
Let’s start by exploring what data is available in the CRANT dataset.
# Get all available annotation fields
available_fields = cp.NeuronCriteria.available_fields()
print(f"Available annotation fields ({len(available_fields)}):")
for field in sorted(available_fields):
print(f" - {field}")
Available annotation fields (25):
- alternative_names
- annotator_notes
- cave_table
- cell_class
- cell_instance
- cell_subtype
- cell_type
- date_proofread
- flow
- hemilineage
- known_nt
- known_nt_source
- nerve
- ngl_link
- nucleus_id
- proofread
- proofreader_notes
- region
- root_id
- side
- status
- super_class
- tract
- user_annotator
- user_proofreader
# Get overview of the dataset
all_annotations = cp.get_all_seatable_annotations()
print(f"Total neurons in dataset: {len(all_annotations):,}")
print(f"Dataset shape: {all_annotations.shape}")
print("\nFirst few rows:")
display(all_annotations.head())
Total neurons in dataset: 6,072
Dataset shape: (6072, 30)
First few rows:
| root_id | root_id_processed | supervoxel_id | position | nucleus_id | nucleus_position | root_position | cave_table | proofread | status | ... | cell_subtype | cell_instance | known_nt | known_nt_source | alternative_names | annotator_notes | user_annotator | user_proofreader | ngl_link | date_proofread | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 576460752700282748 | None | 74170512125421134 | [32782, 30214, 1532] | 72691394107456688 | [37306, 31317, 1405] | [37306, 31317, 1405] | None | False | [DAMAGED, PARTIALLY_PROOFREAD, TRACING_ISSUE] | ... | None | None | acetylcholine | Tanaka et al., 2012 (immuno, mALT, drosophila ... | None | None | [lindsey_lopes] | [lindsey_lopes] | https://spelunker.cave-explorer.org/#!middleau... | None |
| 1 | 576460752681552812 | None | 74100212167609429 | [32121, 31509, 1702] | 72621025497478503 | [36772, 28974, 1953] | [36772, 28974, 1953] | None | True | [BACKBONE_PROOFREAD] | ... | None | None | acetylcholine | Tanaka et al., 2012 (immuno, mALT, drosophila ... | None | None | [lindsey_lopes] | [lindsey_lopes] | https://spelunker.cave-explorer.org/#!middleau... | None |
| 2 | 576460752666303418 | None | 74169069687405059 | [33220, 8787, 4046] | 72620682436952978 | [33727, 8389, 4054] | [33727, 8389, 4054] | None | False | [PARTIALLY_PROOFREAD, TRACING_ISSUE] | ... | None | None | acetylcholine, sNPF | Barnstedt et al. 2016 (immuno, KCs, drosophila... | None | None | [lindsey_lopes] | [lindsey_lopes] | https://spelunker.cave-explorer.org/#!middleau... | None |
| 3 | 576460752722405178 | None | 74100212167388307 | [32442, 31693, 1618] | 72621025497491534 | [36266, 31490, 2021] | [36266, 31490, 2021] | None | False | [PARTIALLY_PROOFREAD, TRACING_ISSUE] | ... | None | None | acetylcholine | Tanaka et al., 2012 (immuno, mALT, drosophila ... | None | None | [lindsey_lopes] | [lindsey_lopes] | https://spelunker.cave-explorer.org/#!middleau... | None |
| 4 | 576460752773799604 | None | 74100280887219649 | [32484, 32119, 1756] | 72691394308791443 | [37240, 29878, 2178] | [37240, 29878, 2178] | None | True | [BACKBONE_PROOFREAD] | ... | None | None | acetylcholine | Tanaka et al., 2012 (immuno, mALT, drosophila ... | None | None | [lindsey_lopes] | [lindsey_lopes] | https://spelunker.cave-explorer.org/#!middleau... | None |
5 rows × 30 columns
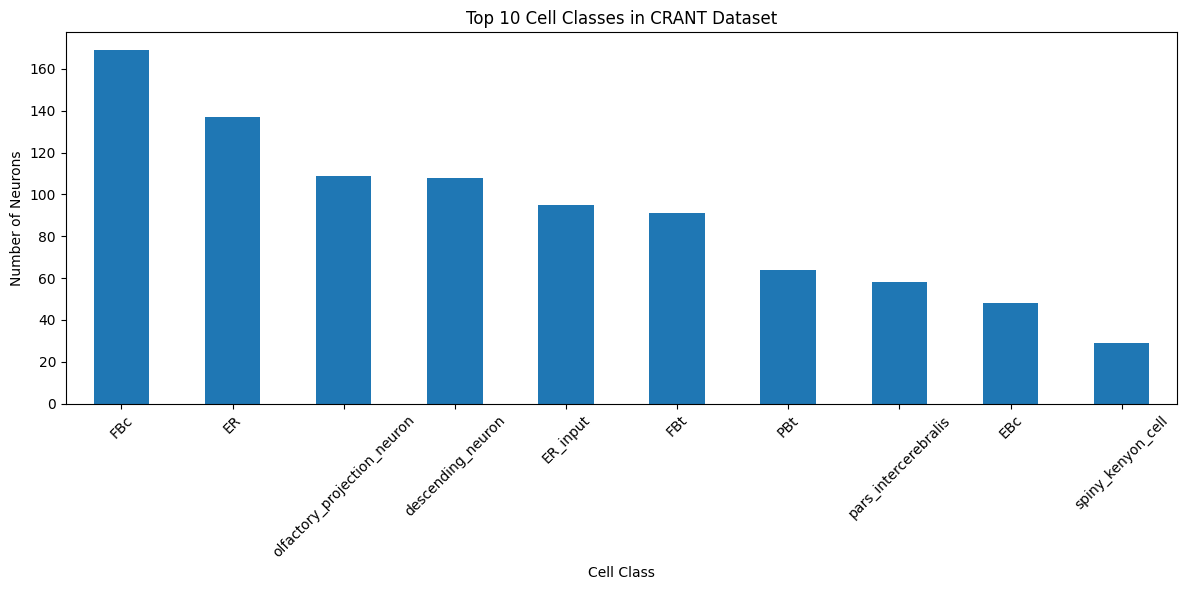
# Explore the distribution of cell classes
cell_class_counts = all_annotations['cell_class'].value_counts()
print("Top 10 cell classes:")
print(cell_class_counts.head(10))
# Visualize
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
cell_class_counts.head(10).plot(kind='bar')
plt.title('Top 10 Cell Classes in CRANT Dataset')
plt.xlabel('Cell Class')
plt.ylabel('Number of Neurons')
plt.xticks(rotation=45)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Top 10 cell classes:
cell_class
FBc 169
ER 137
olfactory_projection_neuron 109
descending_neuron 108
ER_input 95
FBt 91
PBt 64
pars_intercerebralis 58
EBc 48
spiny_kenyon_cell 29
Name: count, dtype: int64
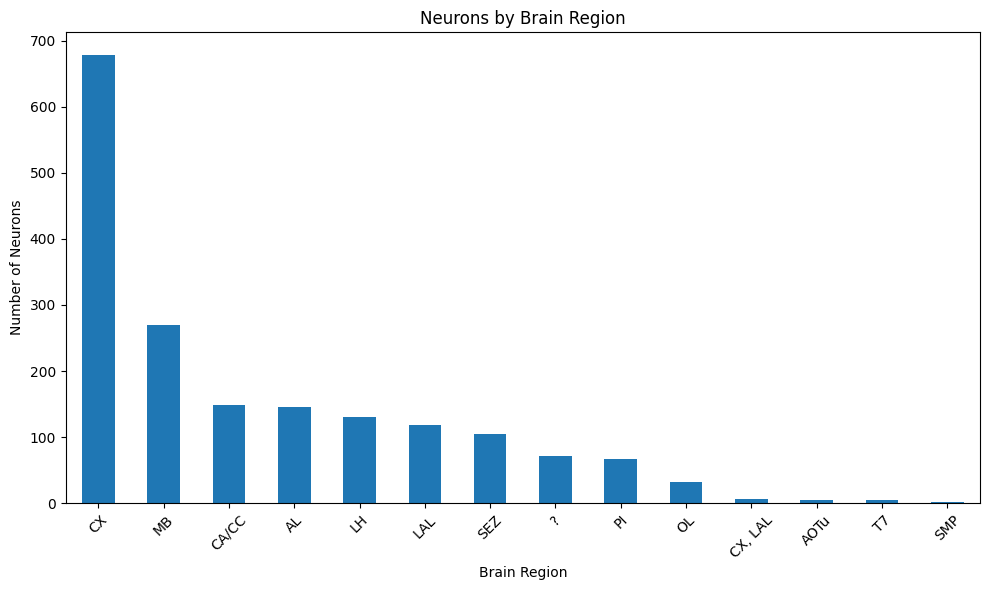
# Explore brain regions
# Each neuron can belong to multiple regions, therefore each entry is a list
from collections import Counter
# Flatten the region lists and count occurrences
region_lists = all_annotations['region'].dropna().tolist()
flat_regions = [region for sublist in region_lists for region in (sublist if isinstance(sublist, list) else [sublist])]
region_counts = pd.Series(Counter(flat_regions)).sort_values(ascending=False)
# Visualize
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
region_counts.plot(kind='bar')
plt.title('Neurons by Brain Region')
plt.xlabel('Brain Region')
plt.ylabel('Number of Neurons')
plt.xticks(rotation=45)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
3. Querying Neurons with NeuronCriteria#
The NeuronCriteria class is the main interface for filtering neurons based on their annotations.
# Query neurons by cell class
olfactory_projection_neuron = cp.NeuronCriteria(cell_class='olfactory_projection_neuron')
opn_ids = olfactory_projection_neuron.get_roots()
print(f"Found {len(opn_ids)} olfactory projection neurons")
# Query with multiple criteria
left_projection_neurons = cp.NeuronCriteria(
cell_class='olfactory_projection_neuron',
side='left'
)
left_pn_ids = left_projection_neurons.get_roots()
print(f"Found {len(left_pn_ids)} left projection neurons")
Found 107 olfactory projection neurons
Found 37 left projection neurons
# Query neurons from specific tracts
malt_neurons = cp.NeuronCriteria(tract='mALT')
malt_ids = malt_neurons.get_roots()
print(f"Found {len(malt_ids)} neurons in mALT tract")
# Get their detailed annotations
malt_annotations = cp.get_annotations(malt_neurons)
print("\nmALT neuron types:")
print(malt_annotations['cell_class'].value_counts())
Found 2275 neurons in mALT tract
mALT neuron types:
cell_class
olfactory_projection_neuron 68
AL_T7_input 5
Name: count, dtype: int64
4. Working with Precomputed Neuron Skeleton and Mesh#
CRANTpy provides access to both precomputed mesh and skeleton representations of neurons. In this section, we’ll see how to retrieve and do basic visualizations of these morphological data.
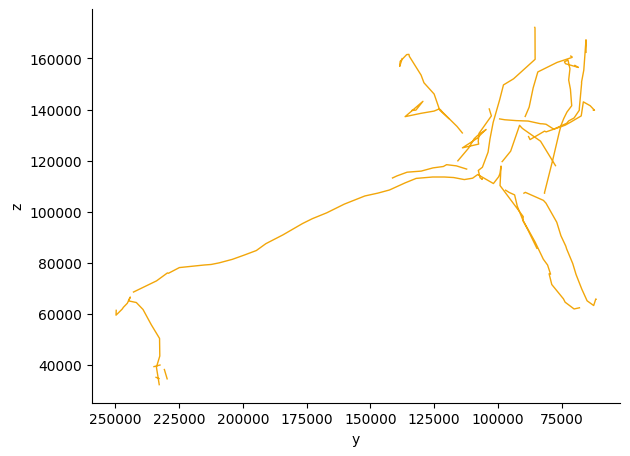
# Get a sample neuron for morphological analysis
sample_neuron_id = opn_ids[0]
# Get the neuron's skeleton - set omit_failures=True to handle problematic neurons gracefully
skeleton = cp.get_skeletons([sample_neuron_id])
print(f"Skeleton properties:")
print(f" Nodes: {len(skeleton.nodes):,}")
print(f" Cable length: {skeleton.cable_length[0]} nm")
Skeleton properties:
Nodes: 221
Cable length: 1075895.125 nm
In order to visualize neurons, we will use the navis library.
import navis
# 2D visualization of skeleton
fig, ax = navis.plot2d(skeleton, view=("-y", "z"), method="2d")
plt.grid(False)
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
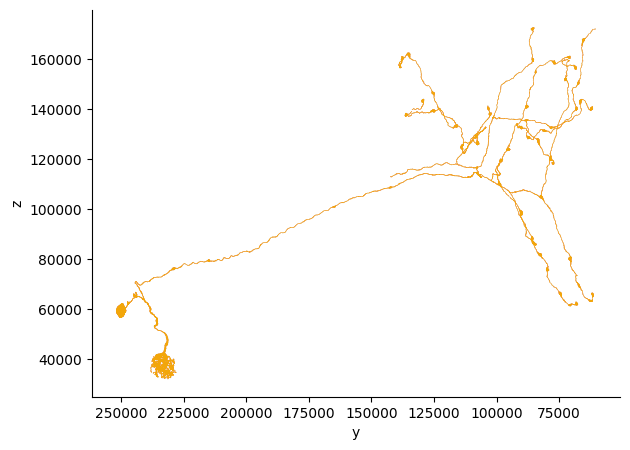
# Get the neuron's mesh
try:
mesh = cp.get_mesh_neuron(sample_neuron_id)
print(f"Mesh properties:")
print(f" Vertices: {len(mesh.vertices):,}")
print(f" Faces: {len(mesh.faces):,}")
print(f" Volume: {mesh.volume:.2f} cubic nanometers")
except Exception as e:
print(f"⚠ Could not get mesh for neuron {sample_neuron_id}: {e}")
print("This may be due to mesh configuration issues in the dataset.")
Mesh properties:
Vertices: 238,432
Faces: 478,609
Volume: 135639679325.33 cubic nanometers
# plot the mesh in 2d using navis
fig, ax = navis.plot2d(mesh, view=("-y", "z"), method="2d")
plt.grid(False)
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# Get skeletons for multiple neurons
sample_opn_ids = opn_ids[:10] # Take first 10 projection neurons
print(f"Attempting to get skeletons for {len(sample_opn_ids)} neurons...")
# Get skeletons with failure handling
try:
opn_skeletons = cp.get_skeletons(sample_opn_ids)
print(f"Successfully obtained {len(opn_skeletons)} skeletons out of {len(sample_opn_ids)} attempts")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error getting skeletons: {e}")
print("⚠ There may be issues with the mesh data for some of these neurons.")
Attempting to get skeletons for 10 neurons...
Successfully obtained 10 skeletons out of 10 attempts
# 2D visualization of all skeletons
fig, ax = navis.plot2d(opn_skeletons, view=("-y", "z"), method="2d")
plt.grid(False)
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
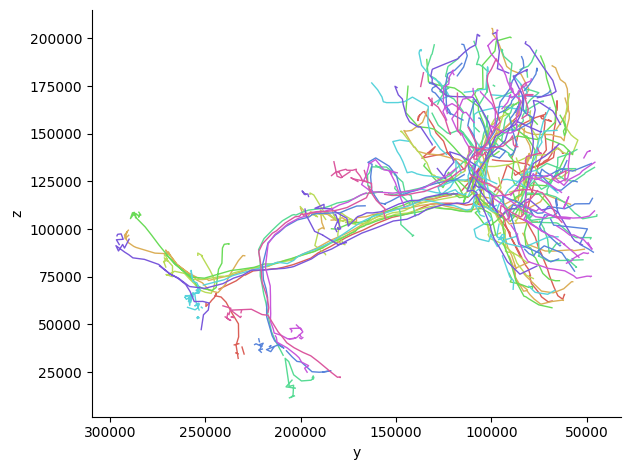
More details on 2D/3D visualization (advanced navis usage, rendering tips, and examples) are available in the deep dive on morphology and visualization — refer to that section for extended guidance.
6. ID Management and Updates#
Neuron IDs can change over time due to proofreading. CRANTpy helps manage these changes.
# Check if our sample IDs are current
sample_ids = opn_ids[:5]
are_current = cp.is_latest_roots(sample_ids)
print(f"Checking {len(sample_ids)} neuron IDs:")
for i, (neuron_id, is_current) in enumerate(zip(sample_ids, are_current)):
status = "Current" if is_current else "⚠ Outdated"
print(f" {neuron_id}: {status}")
Checking 5 neuron IDs:
576460752700282748: Current
576460752681552812: Current
576460752722405178: Current
576460752773799604: Current
576460752656800770: Current
# Update IDs in a DataFrame
# Create a small test DataFrame
test_df = pd.DataFrame({
'root_id': sample_ids,
'analysis_result': np.random.randn(len(sample_ids))
})
print("Original DataFrame:")
display(test_df)
# Update IDs
updated_df = cp.update_ids(test_df, dataset="latest")
print("\nUpdated DataFrame (showing ID update info):")
display(updated_df[['old_id', 'new_id', 'confidence', 'changed']].head())
# replace old ids with new ids
# Replace old IDs with new IDs in test_df
id_map = dict(zip(updated_df['old_id'].astype(str), updated_df['new_id'].astype(str)))
# keep a copy of the original ids
test_df['root_id_original'] = test_df['root_id']
# perform the replacement (preserve values that have no mapping)
test_df['root_id'] = test_df['root_id'].astype(str).map(id_map).fillna(test_df['root_id'])
print("DataFrame after ID replacement:")
display(test_df)
Original DataFrame:
| root_id | analysis_result | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 576460752700282748 | -1.085126 |
| 1 | 576460752681552812 | -2.401884 |
| 2 | 576460752722405178 | 0.262163 |
| 3 | 576460752773799604 | -0.319966 |
| 4 | 576460752656800770 | 0.893296 |
2025-10-04 19:44:48 - WARNING - Multiple supervoxel IDs found for 130 root IDs. Using first occurrence for each.
Updated DataFrame (showing ID update info):
| old_id | new_id | confidence | changed | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 576460752700282748 | 576460752700282748 | 1.0 | False |
| 1 | 576460752681552812 | 576460752681552812 | 1.0 | False |
| 2 | 576460752722405178 | 576460752722405178 | 1.0 | False |
| 3 | 576460752773799604 | 576460752773799604 | 1.0 | False |
| 4 | 576460752656800770 | 576460752656800770 | 1.0 | False |
DataFrame after ID replacement:
| root_id | analysis_result | root_id_original | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 576460752700282748 | -1.085126 | 576460752700282748 |
| 1 | 576460752681552812 | -2.401884 | 576460752681552812 |
| 2 | 576460752722405178 | 0.262163 | 576460752722405178 |
| 3 | 576460752773799604 | -0.319966 | 576460752773799604 |
| 4 | 576460752656800770 | 0.893296 | 576460752656800770 |
10. Summary and Next Steps#
This tutorial has covered the main features of CRANTpy:
✅ Authentication and setup
✅ Exploring the dataset structure
✅ Querying neurons with NeuronCriteria
✅ Accessing morphological data (meshes and skeletons)
✅ 2D visualization
✅ ID management and updates
✅ Advanced querying techniques
Resources#
Happy exploring! 🐜🧠


